what is succinate dehydrogenase Succinate dehydrogenase pathway tca pentose phosphate ppt powerpoint presentation citrate cycle
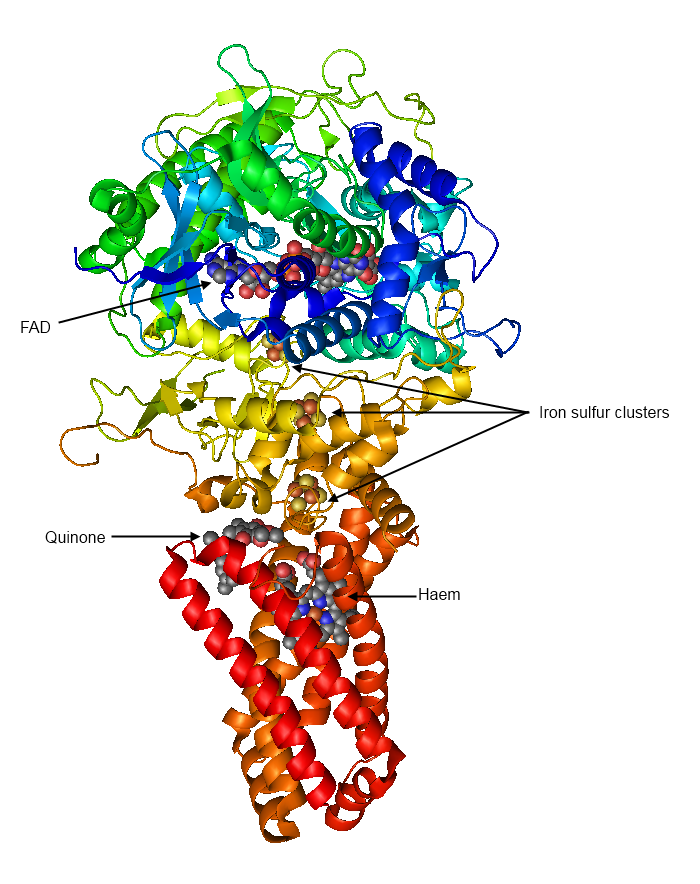
Structure of succinate dehydrogenase [20]. The enzyme is conserved. Succinate dehydrogenase is a key enzyme in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle. This cycle is an essential part of cellular respiration, which produces ATP, the energy currency of the cell. The TCA cycle occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, and involves the conversion of acetyl-CoA into carbon dioxide and high-energy electrons. Succinate dehydrogenase plays a crucial role in this process by catalyzing the conversion of succinate to fumarate, while simultaneously oxidizing FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) to FADH2.
Structure of Succinate Dehydrogenase
![Structure of succinate dehydrogenase [20]](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281167488/figure/fig1/AS:323846247862276@1454222370460/Structure-of-succinate-dehydrogenase-20-The-enzyme-is-conserved-through-evolution-and.png) Succinate dehydrogenase consists of four subunits: A, B, C, and D. Subunits A and B are hydrophilic and located on the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane, while subunits C and D are hydrophobic and embedded within the membrane. Subunit A contains the catalytic site for the oxidation of succinate, while subunit B binds the FAD cofactor. Subunits C and D serve as anchor points for the membrane-bound subunits and facilitate electron transfer within the enzyme.
Succinate dehydrogenase consists of four subunits: A, B, C, and D. Subunits A and B are hydrophilic and located on the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane, while subunits C and D are hydrophobic and embedded within the membrane. Subunit A contains the catalytic site for the oxidation of succinate, while subunit B binds the FAD cofactor. Subunits C and D serve as anchor points for the membrane-bound subunits and facilitate electron transfer within the enzyme.
The structure of succinate dehydrogenase is highly conserved across species, indicating its importance in cellular function. Researchers have determined the three-dimensional structure of succinate dehydrogenase using various techniques such as X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy. These studies have provided valuable insights into the enzyme’s mechanism and function.
TCA Cycle and Pentose Phosphate Pathway
 The TCA cycle, where succinate dehydrogenase is a key player, is closely interconnected with other metabolic pathways in the cell. One such pathway is the pentose phosphate pathway, which generates NADPH and pentose sugars. NADPH is required for various biosynthetic processes, including fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis, while pentose sugars are essential for nucleotide synthesis and other cellular functions.
The TCA cycle, where succinate dehydrogenase is a key player, is closely interconnected with other metabolic pathways in the cell. One such pathway is the pentose phosphate pathway, which generates NADPH and pentose sugars. NADPH is required for various biosynthetic processes, including fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis, while pentose sugars are essential for nucleotide synthesis and other cellular functions.
In addition to its role in energy production, the TCA cycle and pentose phosphate pathway also contribute to the regulation of cellular redox balance and antioxidant defense. The NADH and NADPH produced during these pathways serve as crucial cofactors for redox reactions in the cell, protecting it from oxidative damage caused by reactive oxygen species.
Understanding the structure and function of enzymes like succinate dehydrogenase is of great importance in both basic research and applied fields. Researchers studying mitochondrial diseases, cancer metabolism, and drug development target succinate dehydrogenase and other TCA cycle enzymes to gain insights into disease mechanisms and identify potential therapeutic targets.
In conclusion, succinate dehydrogenase is a vital enzyme in the TCA cycle, involved in energy production, cellular redox balance, and antioxidant defense. Its conserved structure and function across species highlight its significance in cellular metabolism. Further research on succinate dehydrogenase and related enzymes will continue to unravel its role in health and disease, opening doors for potential therapeutic interventions.
If you are searching about The structure of complex II (succinate dehydrogenase). This enzyme you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Pics about The structure of complex II (succinate dehydrogenase). This enzyme like Structure of succinate dehydrogenase [20]. The enzyme is conserved, The structure of complex II (succinate dehydrogenase). This enzyme and also Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) complex in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA. Read more:
The Structure Of Complex II (succinate Dehydrogenase). This Enzyme
 www.researchgate.netsuccinate dehydrogenase enzyme oxidative tca phosphorylation fad subunit
www.researchgate.netsuccinate dehydrogenase enzyme oxidative tca phosphorylation fad subunit
The Product Of Succinate Dehydrogenase Is Ubiquinol Not Reduced Flavin
 www.polypompholyx.comdehydrogenase succinate enzyme sdh ubiquinol reduced flavin
www.polypompholyx.comdehydrogenase succinate enzyme sdh ubiquinol reduced flavin
Structure Of Succinate Dehydrogenase [20]. The Enzyme Is Conserved
![Structure of succinate dehydrogenase [20]. The enzyme is conserved](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281167488/figure/fig1/AS:323846247862276@1454222370460/Structure-of-succinate-dehydrogenase-20-The-enzyme-is-conserved-through-evolution-and.png) www.researchgate.netsuccinate dehydrogenase structure enzyme conserved fad sdha binding bound heme
www.researchgate.netsuccinate dehydrogenase structure enzyme conserved fad sdha binding bound heme
Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH) Complex In The Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA
 www.researchgate.netdehydrogenase succinate tca sdh tricarboxylic electron
www.researchgate.netdehydrogenase succinate tca sdh tricarboxylic electron
PPT - TCA & Pentose Phosphate Pathway 12/01/2009 PowerPoint
 www.slideserve.comsuccinate dehydrogenase pathway tca pentose phosphate ppt powerpoint presentation citrate cycle
www.slideserve.comsuccinate dehydrogenase pathway tca pentose phosphate ppt powerpoint presentation citrate cycle
Succinate dehydrogenase pathway tca pentose phosphate ppt powerpoint presentation citrate cycle. Succinate dehydrogenase structure enzyme conserved fad sdha binding bound heme. Succinate dehydrogenase enzyme oxidative tca phosphorylation fad subunit